7 Solutions to Reduce Waste in the Microbiology Laboratory
Waste reduction: a hot topic in microbiology labs!
How do we know? Because most SuperMicrobiologists are working on it!
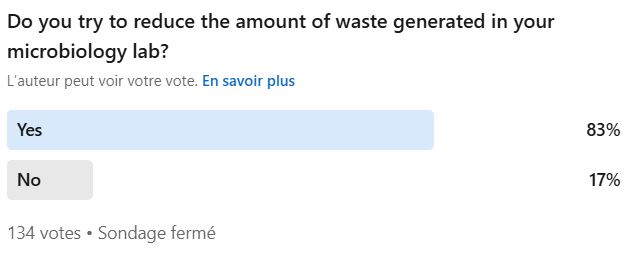
Honestly, we would have bet our hand on a Bunsen burner that it was all about cutting costs (since HCRW disposal isn’t cheap).
But no! Surprise, surprise — it seems that ecology is leading the charge. If that’s truly the case, we’ll give a round of applause… with our burned hand.
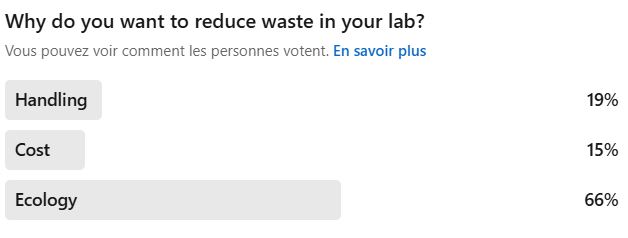
After touring labs and talking with some of the best SuperMicrobiologists, we’ve discovered several clever ways to reduce your waste.
In this article, we’ll introduce you to 7 practical solutions to go green.
Content :
- Cut your BPW volumes by 2.5
- Replace serial dilution glass tubes
- Reduce the number of tubes and Petri dishes
- Replace Petri dishes with much “lighter” alternatives
- Donate expired reagents
- Composting/Methanizing Food Samples
- Reusing Pipette Tips
What is HCRW ?

Health-Care Risk Waste (HCRW), also known as Infectious Medical Waste (IMW), Infectious Healthcare Waste (IHW) or Biohazardous Waste, refers to waste that may be contaminated with infectious agents like bacteria or viruses. If not properly managed, it can pose a serious risk to public health.
HCRW must be collected, stored, and disposed of using specific procedures (like incineration) to prevent the spread of infections.
Managing HCRW is expensive due to the logistics, regulations, specialized equipment, and training required to ensure these wastes do not endanger public health.
We all have those yellow bins (or bags) in our labs… Now, let’s see how we can reduce their size!
1 – Cut your BPW volumes by 2.5: PIF Supplement by Bio-Rad

The PIF Supplement developed by Bio-Rad reduces the dilution of food samples in Buffered Peptone Water (BPW) from 1:10 to 1:4.
The Supplement is directly added to the BPW used for the detection of Cronobacter, Salmonella, Enterobacteriaceae, and STEC.
Imagine the waste reduction!
- For 100 samples of 25g, the EPT volume goes from 22.5 liters to 5.6 liters, saving around 17 liters.
- For 100 samples of 375g, the savings reach 225 liters of EPT.
The reduction in waste (and therefore HCRW) adds up to thousands of liters per year… and that’s also less weight to lift!
Other Benefits of the PIF Supplement :
- Certified
AFNOR and AOAC certified for low-moisture products (like flour, milk powder, and other dry powders). - One broth, multiple targets
With a single broth (EPT + PIF supplement), you can test for multiple pathogens, including Cronobacter, Salmonella, Enterobacteriaceae, and STEC. - Fewer musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs)
By reducing the volume of broth to prepare, the workload for technicians is lighter. For 375g samples, the bag weighs only 1.5 kg instead of the usual 3.75 kg. - Flexible detection methods
After 18-20 hours of incubation, detection can be done by PCR (iQ-Check method) or chromogenic media (RAPID’Chromogenic). - Color indicator
The supplement is blue, making it easy to visually check that it has been added correctly.
2 – Replace serial dilution glass tubes: Inlabtec Serial Diluter

This system makes it easier to perform and standardize serial dilutions. But it has another key benefit, it helps reduce waste volume.
Heavy glass tubes are replaced with plastic bags, which are much lighter and take up less space than glass.
Other advantages of the Inlabtec Serial Diluter:
- Automatic homogenization
No need for a vortex! The serial diluter ensures perfectly homogeneous and reproducible dilutions every time. - Optimized ergonomics
Say goodbye to tubes, caps, and repetitive opening/closing movements. Simply add the sample into the bag, reducing the risk of musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs). - Maximum reliability (or almost!)
A light clearly indicates which bag to use at each step, guiding the operator step by step to minimize errors.
3 – Reduce the number of tubes and Petri dishes: Interscience Spiral Platers

Here’s another device that automates serial dilutions. The spiral plater allows for 3 dilutions on a single Petri dish, significantly reducing the need for both tubes and Petri dishes.
Other advantages of the Interscience Easy Spiral:
- Fewer dilutions, more efficiency
With just one Petri dish, you can cover 3 dilutions and achieve a counting range of 100 to 1 x 10⁷ CFU/mL. - Automation
Reduces the risk of human error. - Consistent and uniform plating
No more “spreader” for plating! The automatic spiral plater ensures a uniform and reproducible distribution of the sample. - The easySpiral Dilute version goes even further
This version automates up to 5 serial dilutions (1/10 each) before spiral plating. It can handle samples with up to 10¹² CFU/mL.
4 – Replace Petri dishes with much “lighter” alternatives


Do we still need to introduce Petrifilms? These are thin sheets containing a culture medium (selective or not) that can be used as an alternative to traditional Petri dishes.
Their main advantage? They are extremely thin and lightweight (about the thickness of a sheet of paper), which means they take up far less space in the waste bins.
But Petrifilm is no longer alone. In recent years, other similar solutions have hit the market, such as Media Pad and Compact Dry.
5 – Donate expired reagents
What can you do with expired Petri dishes?
Instead of throwing them away, why not donate them to a local university?
Less waste, happy students and teachers — it’s a win-win situation!
6 – Composting/Methanizing Food Samples
What should food microbiology laboratories do with the tons of food samples they receive for analysis?
For example, a French laboratory has collaborated with a local association to set up a composter.
And what about meat samples? They’ve established a partnership with a zoo, which uses the meat to feed large felines, among others.
7 – Reusing Pipette Tips
Here’s another initiative from a french laboratory. They launched an internal project to clean, sterilize, and reuse pipette tips.
The feasibility study has already been completed, and the results are quite positive.
Could the return of the reusable glass Petri dish be next?
If you know of any other technologies or tips to reduce waste, feel free to share them!
If you know of other technologies or tips to reduce waste, feel free to share them in the comments. We’d be happy to include them in the next update of this article.













Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!